Table of Contents
Noonan Syndrome
Main Features
- Highly variable but most have short stature, mild intellectual disability or developmental delay and
- Characteristic faces
- High forehead
- depressed nasal bridge
- low-set posteriorly rotated ears with fleshy helices
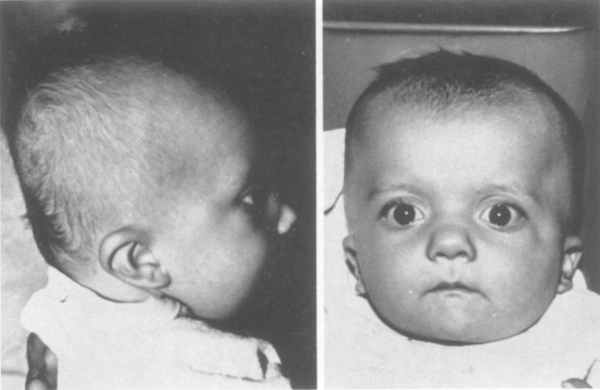
 Photos from J Med Genet. 1987;24(1):9-13.
Photos from J Med Genet. 1987;24(1):9-13.
Eye Findings
- Refractive Errors: Myopia, hyperopia and astigmatism
- Ptosis
- Hypertelorism
- Downslanting palpebral fissures
- Epicanthal folds
- Keratoconus
- vivid blue or blue-green iris
- Posterior embryotoxin
- Cataract
- Strabismus
- Nystagmus
- Optic nerve hypoplasia
- Optic nerve coloboma
Other Findings
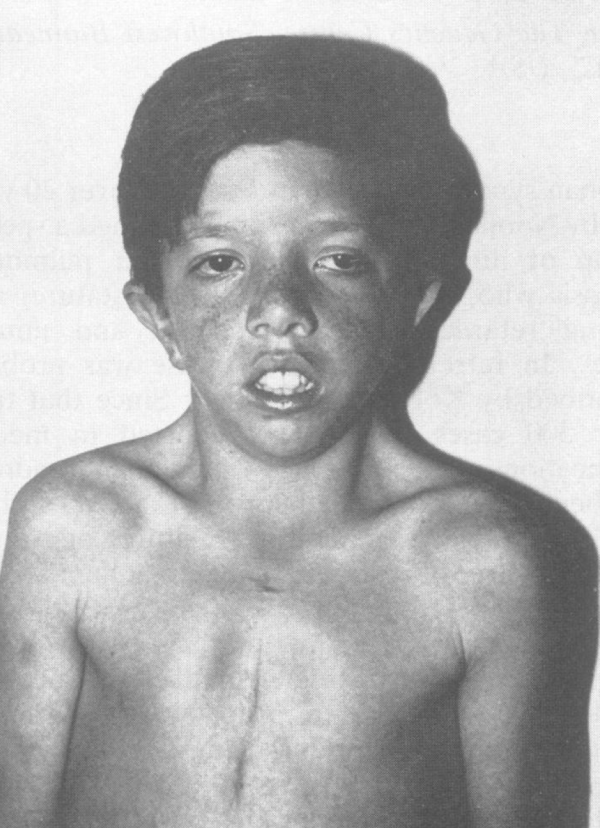
- Webbed or broad neck
- Chiari Malformation
- Hydrocephalus
- Macrocephaly
- Craniosynostosis
- Sensorineural deafness
- Conductive hearing loss
- Giant cell tumors of the jaw
- Sternal deformities
- pectus carinatum of the superior sternum
- pectus excavated of the inferior sternum
- Cardiovascular defects
- Pulmonic stenosis
- hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- ASD
- VSD
- lymphatic dysplasia
- Chyptorchidism
- Infertility
- Hematologic abnormalities
- elevation in PT/PTT
- abnormal platelets, count and function
Etiology
- Genetic disorder of the genes in the RAS-MAPK pathway
- PTPN11 (50%)
- SOS1 (13%)
- RAF1 (5%)
- RIT1 (5%)
- others
- KRAS, BRAF, LZTR1, NRAS
- This pathway is important in cellular differentiation and proliferation
- Autosomal dominant inheritance most commonly with 2/3 denovo
- Associated with advanced paternal age